
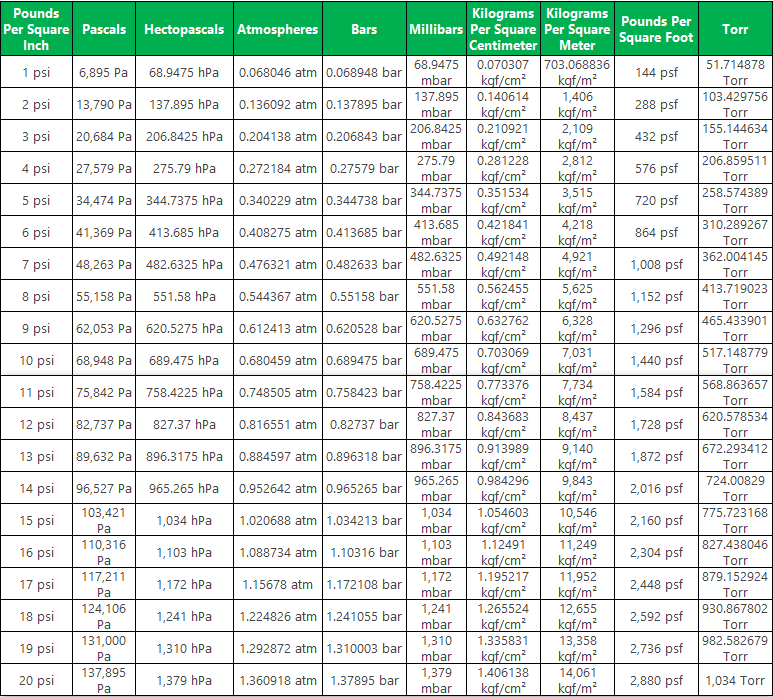
The converse is pound per square inch gauge ( psig), indicating that the pressure is relative to atmospheric pressure. Since atmospheric pressure at sea level is around 14.7 psi (101 kilopascals), this will be added to any pressure reading made in air at sea level. The pound per square inch absolute ( psia) is used to make it clear that the pressure is relative to a vacuum rather than the ambient atmospheric pressure. In SI units, 1 psi is approximately 6,895 pascals. It is the pressure resulting from a force with magnitude of one pound-force applied to an area of one square inch. The pound per square inch (abbreviation: psi) or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch (symbol: lbf/in 2), is a unit of measurement of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units. Although the pascal is more widely used in scientific contexts, psi is more often used in everyday contexts, particularly in countries like the United States as well as others under the US customary or imperial systems of units.ġ5 bar = 15 × 14.503773773 psi = 217.A pressure gauge reading in psi (red scale) and kPa (black scale) As such, the prototype pound at the time was known as the avoirdupois wool pound.Ĭurrent use: The psi is fairly widely used to measure numerous pressures, such as tire pressure, scuba tank pressure, natural gas pipeline pressure, among others. The system is believed to have come into use in England around 1300 and was used in the international wool trade. It is based on the avoirdupois system, a system that uses weights in terms of the avoirdupois pound, which was standardized in 1959. History/origin: Pound-force per square inch is a unit that originated in the imperial and US customary systems of units. One psi is approximately 6,895 pascals (N/m 2). It is defined as the pressure that results when a force of one pound-force is applied to a one-square-inch area. Pound-force per square inchĭefinition: A pound-force per square inch (symbol: psi) is an imperial and US customary unit of pressure based on avoirdupois units. Meteorologists and weather reporters worldwide often use this unit for convenience, since working in pascals would result in much larger values. Millibars (symbol: mb) are also commonly used when referencing atmospheric air pressure, where atmospheric pressure equals 1013.25 mbar (101.325 kPa). The International Bureau of Weights and Measures has specified the bar as a unit that authors should have the freedom to use but has chosen not to include the bar in the list of non-SI units accepted for use with SI. The term "bar" comes from the Greek word "baros," which means weight.Ĭurrent use: Although the bar is a metric unit of pressure, it is not accepted within the International System of Units (SI) and is even deprecated within certain fields.

History/origin: The unit, bar, was introduced by Vilhelm Bjerknes, a Norwegian meteorologist who founded modern weather forecasting. It is equal to 0.987 atmospheres (101,325 Pa), the unit often used as a reference of standard pressure. Definition: A bar (symbol: bar) is a metric unit of pressure that is defined as exactly 100,000 pascals (symbol: Pa).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
